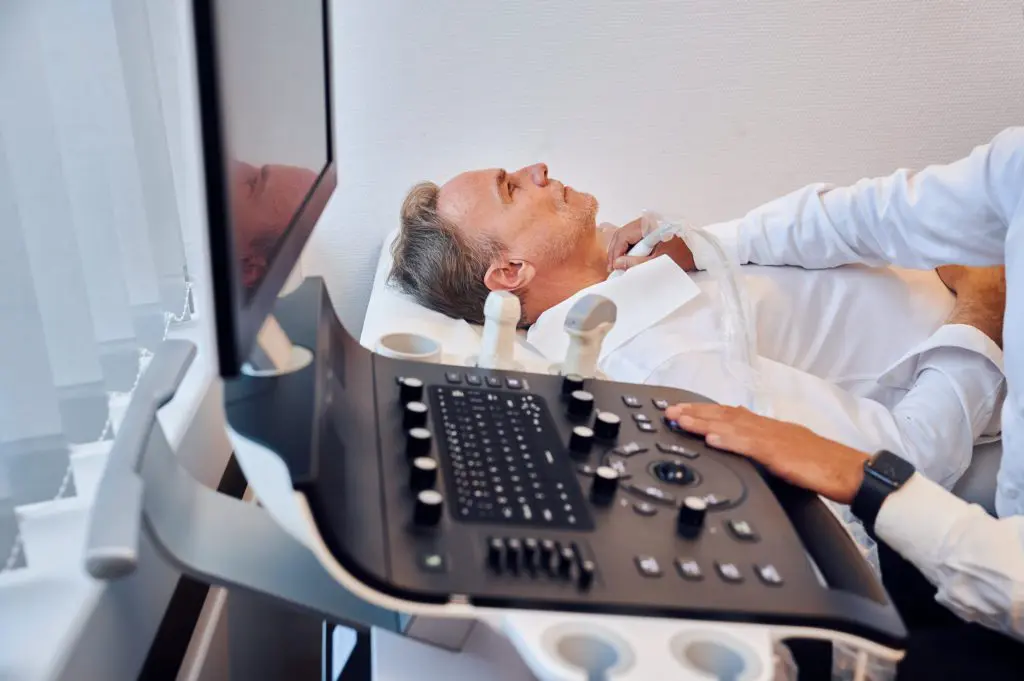
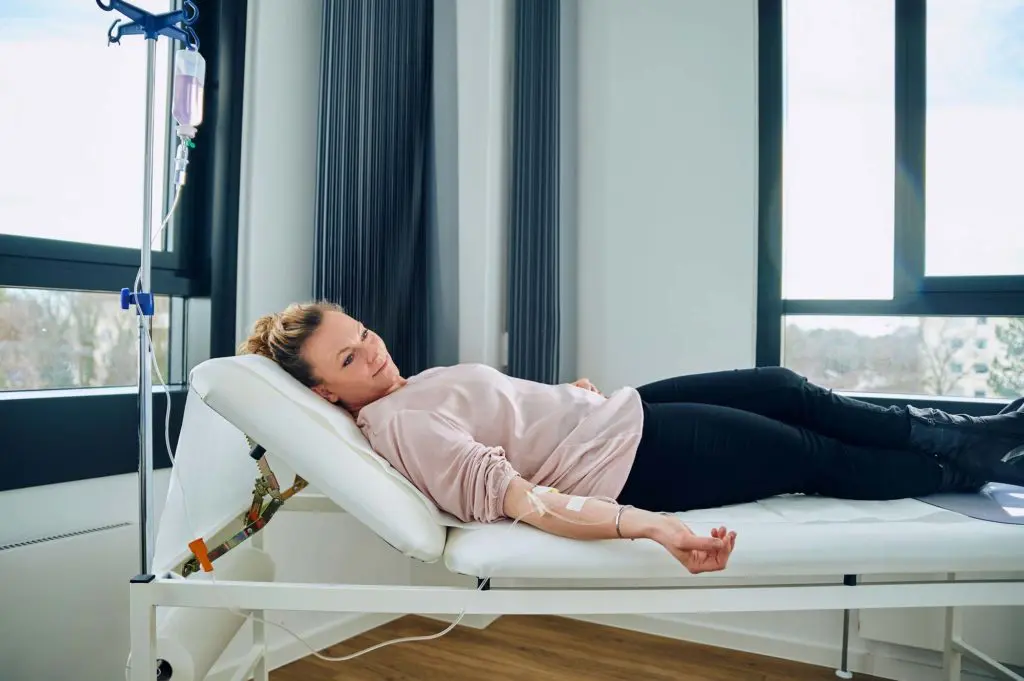
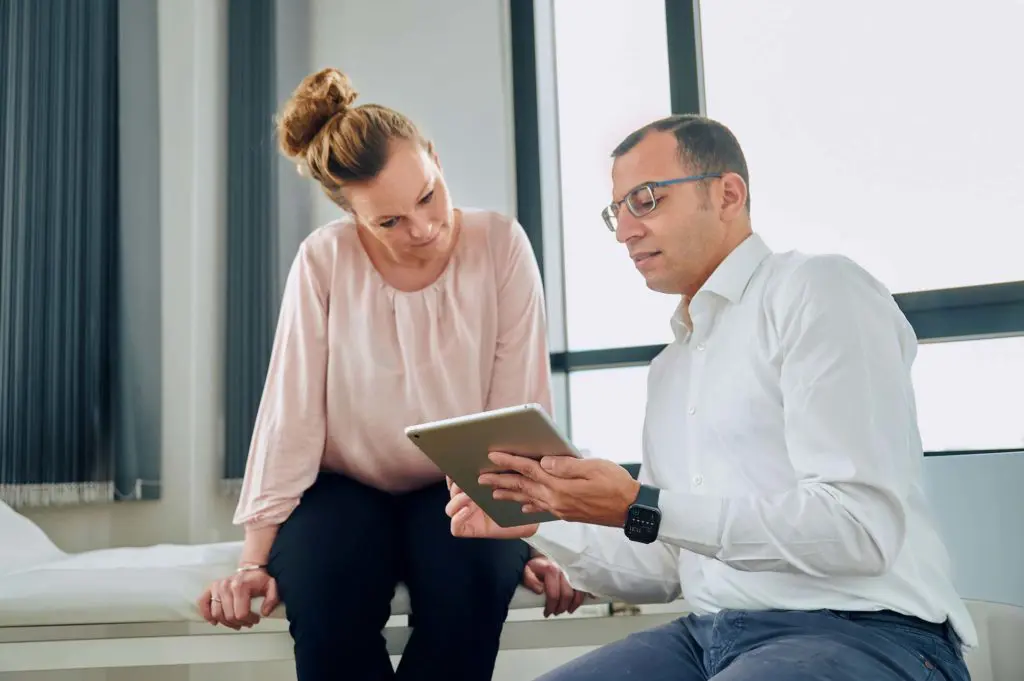
- Get healthy
Overview
DigestionPsyche & SoulMusculoskeletal systemHormonesCirculationRespiratory systemHead & NervesSkin - Stay healthy
Overview
CoronavirusPreventive MedicineNutritional MedicineCancer Prevention & Early DetectionCheck-UpsTravel medicineVaccinations - hybrid practicePracticesGeneral
- News
- CareerOverview
- Service